Introduction
Bulldozers Working: Powering Through Earth and History.Bulldozers have become synonymous with powerful earthmoving machines, revolutionizing the construction, mining, and agricultural industries. These heavy-duty vehicles play a pivotal role in shaping landscapes, clearing debris, and performing various tasks that would otherwise be incredibly labor-intensive. In this article, we will explore the world of bulldozers, from their historical origins to their modern-day applications, technology advancements, and environmental impact.
What are Bulldozers and How Do They Work?

Definition of Bulldozers
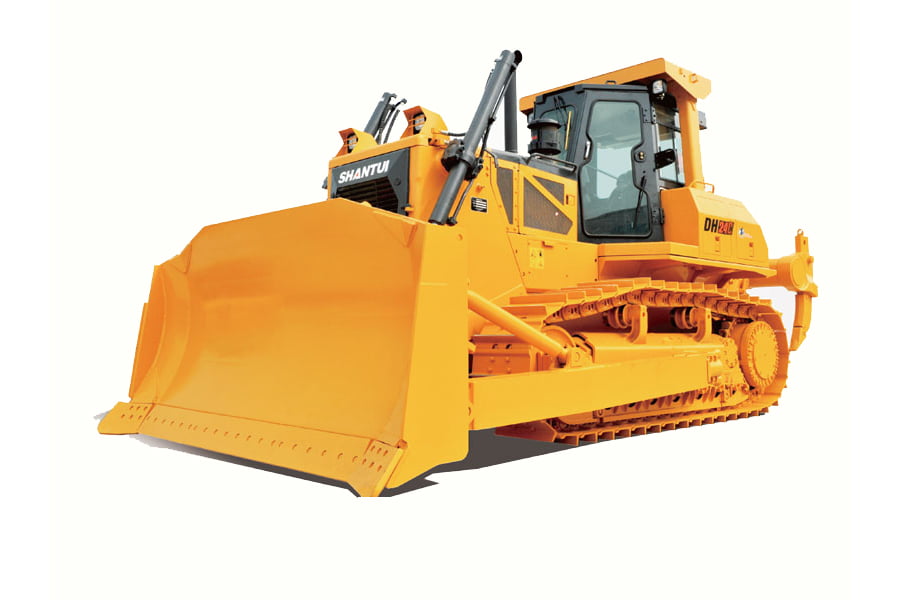
Bulldozers are powerful and heavy-duty earthmoving machines widely used in construction, mining, and other industries. They are equipped with a large metal plate, known as a blade, positioned at the front, which can be adjusted to different angles hydraulically. This design enables bulldozers to efficiently push or move massive quantities of materials, including soil, sand, debris, and rocks, with ease. The immense strength and versatility of bulldozers make them indispensable in various applications, where their ability to clear, level, and shape terrain significantly enhances productivity and efficiency. These robust machines have revolutionized the way we approach earthmoving tasks, enabling us to tackle large-scale projects with precision and effectiveness. With continuous advancements in technology, bulldozers continue to evolve, becoming more environmentally friendly, automated, and efficient, promising a bright future for the construction and earthmoving industries.
Components and Mechanism
The components and mechanism of bulldozers are integral to their exceptional performance and versatility. These heavy-duty machines consist of several key components that work together to ensure efficient operation and maneuverability.
- Engine: At the heart of every bulldozer is a powerful engine that provides the necessary horsepower and torque to drive the machine. These engines are designed to withstand demanding work environments and provide the raw power required to move massive amounts of material.
- Tracks or Wheels: Bulldozers come in two main configurations: crawler bulldozers with continuous tracks and wheeled bulldozers with tires. Crawler bulldozers are equipped with tracks that distribute the machine’s weight evenly, offering superior traction and stability. Wheeled bulldozers, on the other hand, have wheels that provide better mobility on smoother surfaces.
- Blade: The most crucial component of a bulldozer is the blade, also known as the dozer blade. It is a large metal plate mounted on the front of the machine, and its design may vary depending on the intended application. The blade can be straight for pushing material, U-shaped for carrying loose materials, or even equipped with a ripper at the rear for breaking up hard surfaces.
The History of Bulldozers
Origins and Early Developments
The origins and early developments of bulldozers trace back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries when there was a growing need for more efficient earthmoving solutions. The concept of using heavy equipment to move earth and materials dates back even further to ancient times, where human labor and animals were employed for manual excavation and construction tasks.
- Early Earthmoving Devices: Before the invention of modern bulldozers, various primitive earthmoving devices were used. In ancient Egypt, for instance, workers utilized levers, wooden sledges, and animal power to move heavy stones and construct monumental structures like the pyramids. Similarly, ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley relied on manual labor and animal-driven plows to prepare agricultural fields and create irrigation channels.
- Caterpillar Tractors and Holt Manufacturing Company: The advent of the industrial revolution in the late 19th century brought significant advancements in machinery and technology. In the early 1900s, Benjamin Holt, an American inventor and founder of the Holt Manufacturing Company, developed and patented the first successful track-type tractor. These tractors, later known as “caterpillar tractors,” utilized continuous tracks instead of wheels, providing better traction and reducing ground pressure. The tracks allowed the tractors to move efficiently across soft and muddy terrains, making them invaluable for agricultural tasks.
- The Emergence of Bulldozers: In the early 20th century, several modifications and improvements were made to the caterpillar tractors, eventually leading to the creation of the bulldozer as we recognize it today. The concept of fitting a large, heavy-duty blade to the front of the tractor to move soil and other materials quickly gained popularity. The term “bulldozer” itself is believed to have originated from the combination of “bull,” referring to the powerful nature of the machine, and “dozer,” meaning to push or move material.
- Development in Construction and Military Use: As the construction and mining industries grew, so did the demand for more powerful earthmoving equipment. The introduction of bulldozers with blades significantly improved the efficiency of construction projects by enabling quick land clearing, excavation, and leveling. During World War I, bulldozers were adapted for military engineering tasks, such as constructing trenches and clearing obstacles on the battlefield.
- Continued Advancements: Over the years, bulldozers underwent further advancements in design, power, and versatility. Hydraulic systems were incorporated, allowing for more precise control of the blade’s movement. Bulldozers also became available in various sizes and configurations to cater to different industries and applications.
Advancements and Modern Use
Advancements in bulldozer technology have propelled these earthmoving machines into a new era of efficiency, precision, and versatility. Over the years, continuous research and development efforts have resulted in groundbreaking innovations that have transformed the modern use of bulldozers across various industries.
- Hydraulic Systems and Control: One of the most significant advancements in bulldozer technology is the integration of sophisticated hydraulic systems. Hydraulic cylinders and pumps allow for precise control of the blade’s movement, enabling operators to adjust the angle, height, and tilt of the blade with ease. This level of control enhances the bulldozer’s ability to tackle intricate grading tasks and handle diverse materials with accuracy.
- Power and Performance: Bulldozers have seen considerable improvements in power and performance. Today’s bulldozers are equipped with robust engines that deliver higher horsepower and torque, allowing them to effortlessly move heavier loads and operate in challenging terrains. These powerful machines can efficiently handle demanding tasks, increasing productivity on construction sites and in mining operations.
- Operator Comfort and Safety: The modern bulldozer’s operator cabin has undergone significant enhancements to prioritize comfort and safety. Ergonomically designed controls, adjustable seats, and improved visibility contribute to reduced operator fatigue and increased efficiency during long working hours. Moreover, safety features, such as rollover protection structures (ROPS) and falling object protection structures (FOPS), have been integrated to protect operators from potential hazards.
- GPS Technology and Automation: One of the most transformative advancements in recent years is the integration of Global Positioning System (GPS) technology into bulldozers. GPS-equipped bulldozers can access digital terrain models, enabling them to perform precise grading and leveling based on pre-programmed designs. Automation further streamlines the grading process, reducing human error and ensuring consistent results.
- Versatility and Attachments: Modern bulldozers are designed to accommodate a wide range of attachments, expanding their applications beyond traditional earthmoving tasks. Some common attachments include rippers, winches, and even specialized blades for specific tasks like fine grading or heavy rock removal. This versatility allows bulldozers to adapt to various projects, from road construction to environmental restoration.
- Environmental Considerations: With growing awareness of environmental impact, bulldozer manufacturers have focused on developing more eco-friendly models. Hybrid bulldozers, incorporating both diesel engines and electric motors, have emerged as greener alternatives that reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, efforts are being made to explore fully electric bulldozers powered by renewable energy sources.
Modern Use of Bulldozers:
In the modern era, bulldozers are indispensable across several industries due to their diverse applications and impressive capabilities:
- Construction: Bulldozers are extensively used in construction projects for site preparation, grading, and land clearing. They play a crucial role in preparing the terrain for building foundations, roads, and infrastructure.
- Mining: In the mining industry, bulldozers are instrumental in excavating and transporting large quantities of minerals and ores. Their robust build and powerful blades enable efficient operations in mining and quarrying activities.
- Infrastructure Development: Bulldozers are essential for infrastructure development, such as building dams, reservoirs, and canals. They are also used in the maintenance and expansion of existing infrastructure.
- Agriculture: In agriculture, bulldozers assist in land clearing, creating irrigation channels, and leveling fields for efficient farming practices. They contribute significantly to enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Forestry: In the forestry sector, bulldozers are employed to clear land for plantations, access remote areas, and assist in forest management operations.
- Disaster Relief: Bulldozers play a critical role in disaster relief efforts, helping to clear debris and create access routes in the aftermath of natural disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes.
The modern use of bulldozers continues to evolve as technology advances and industries seek more efficient and sustainable solutions. From their historical roots as modified farm tractors to their current state-of-the-art designs, bulldozers remain an essential part of various industries, shaping the landscapes we inhabit and the infrastructure we rely on. As the demand for efficient construction and earthmoving equipment grows, bulldozer technology will undoubtedly continue to evolve, promising a future of even greater performance and environmental responsibility.
Bulldozers Working:Types of Bulldozers
Crawler Bulldozers
Crawler bulldozers, also known as track-type bulldozers, are a specialized type of bulldozer that has revolutionized earthmoving and construction operations. These robust machines are equipped with continuous tracks rather than wheels, offering unique advantages that make them indispensable for specific tasks and challenging terrains.
- Superior Traction and Stability: One of the key advantages of crawler bulldozers is their superior traction and stability. The continuous tracks distribute the machine’s weight evenly over a larger surface area, reducing ground pressure. This design allows them to navigate through soft and uneven terrains, such as mud, sand, and loose soil, with minimal risk of getting stuck.
- Versatility in Various Terrains: Crawler bulldozers are highly versatile and adaptable to a wide range of terrains. Whether it’s navigating through rugged landscapes in mountainous regions or swampy marshlands, these machines excel in areas where wheeled bulldozers may struggle due to their limited traction.
- Increased Pushing Power: The continuous tracks of crawler bulldozers provide excellent traction, enabling them to generate substantial pushing power. This makes them highly efficient for pushing heavy loads, such as boulders, rocks, and debris, without losing traction or stability.
- Low Ground Disturbance: In projects that require minimal ground disturbance, such as site grading in sensitive environmental areas, crawler bulldozers are preferred. The wide surface area of their tracks helps distribute the machine’s weight more evenly, reducing the risk of damaging the underlying terrain.
- Ideal for Heavy-Duty Operations: Crawler bulldozers are the go-to choice for heavy-duty earthmoving and construction tasks. Their robust build and rugged construction make them well-suited for handling demanding applications, such as large-scale mining, quarrying, and infrastructure projects.
- Precise Control with Modern Technology: Advancements in technology have further enhanced the performance of crawler bulldozers. Hydraulic systems, combined with GPS technology, provide operators with precise control over the blade’s movements and allow for accurate grading and leveling.
Wheeled Bulldozers
Wheeled bulldozers, also known as wheel-type bulldozers, are a specialized variant of bulldozers that offer distinct advantages in certain applications and environments. Unlike their crawler counterparts, wheeled bulldozers are equipped with wheels, making them more suitable for specific terrains and tasks that require enhanced mobility and speed.
- High Mobility and Maneuverability: Wheeled bulldozers are renowned for their high mobility and maneuverability. The use of wheels allows them to travel at faster speeds on smooth or paved surfaces, making them ideal for projects that require frequent relocation or tasks covering large areas.
- Versatility on Hard Surfaces: Wheeled bulldozers excel on hard surfaces, such as roads, highways, and urban construction sites. Their wheels provide a smooth ride, reducing the impact on paved surfaces and ensuring minimal damage to finished roads during maintenance or construction work.
- Compact Design and Lower Ground Pressure: Wheeled bulldozers typically have a more compact design compared to their crawler counterparts. This attribute results in a lower ground pressure, making them suitable for projects where minimal ground disturbance is essential, such as landscaping and turf management.
- Efficient for Lighter Loads: Wheeled bulldozers are well-suited for lighter loads and tasks that do not require the brute force provided by crawler bulldozers. Their agility and faster speeds make them efficient for applications like site clean-up, debris removal, and general material handling.
- Easy Transportation: Wheeled bulldozers can be transported more easily between job sites compared to crawler bulldozers. They can be driven on public roads without causing damage to the pavement, eliminating the need for additional transportation equipment.
- Excellent for Urban Construction: In urban construction projects where maneuvering within confined spaces is crucial, wheeled bulldozers shine. Their ability to navigate tight areas and their faster speed make them valuable assets in urban settings.
Bulldozer Applications and Uses
Construction and Infrastructure
One of the primary applications of bulldozers is in construction and infrastructure projects. They are instrumental in site preparation, grading, and foundation work. Bulldozers can efficiently clear land and create level surfaces, ensuring a stable base for further construction.
Mining and Landscaping
Bulldozers play a vital role in mining operations, where they are used for excavation and moving large quantities of minerals and ores. Additionally, they find application in landscaping projects, such as shaping golf courses and recreational areas.
Agriculture and Forestry
In the agricultural sector, bulldozers help clear fields, create irrigation channels, and prepare land for cultivation. Moreover, in forestry, they are used to clear land for plantations and access difficult terrains.
Key Features of Bulldozers
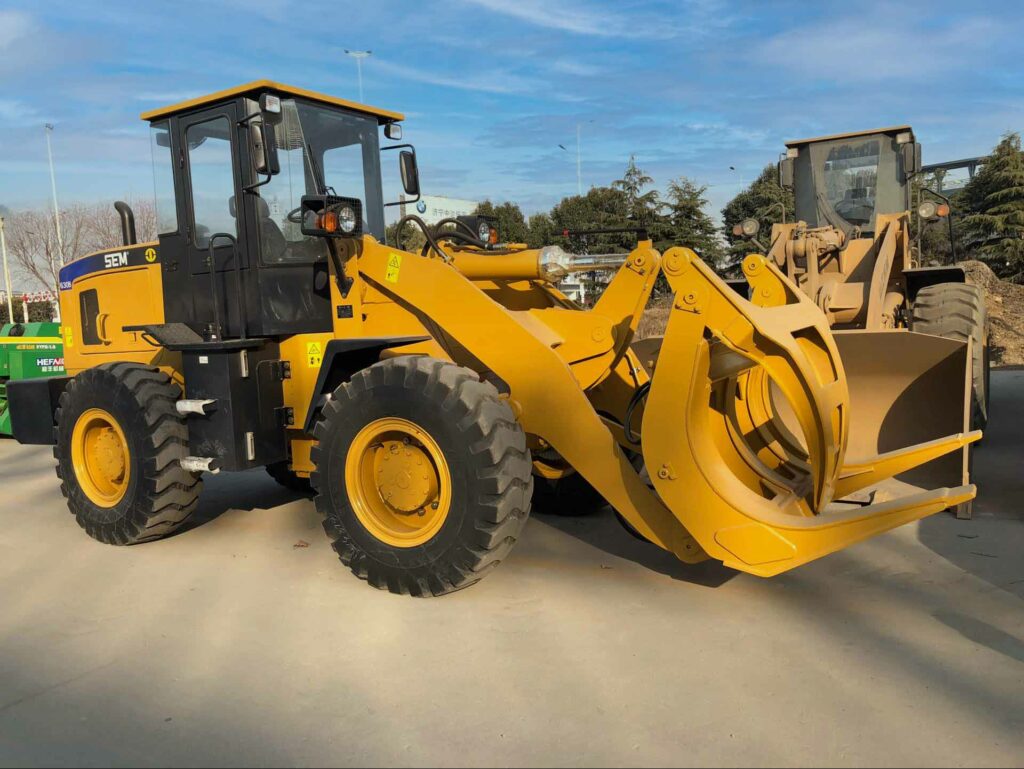

Blades and Attachments
The blade is the most critical component of a bulldozer, and various blade types serve different purposes. Straight blades are ideal for pushing materials, while U-blades are excellent for carrying and spreading loose material. Additionally, bulldozers can be equipped with rippers at the rear to break hard surfaces.
Power and Performance
Bulldozers are equipped with powerful engines that provide high torque and traction. This ensures they can handle heavy loads and challenging terrains with ease. Modern bulldozers also incorporate advanced hydraulic systems for precise blade control.
Operating a Bulldozer
Safety Measures
Operating a bulldozer requires proper training and adherence to safety protocols. The operator must wear appropriate protective gear and be aware of potential hazards on the worksite. Regular maintenance and inspections are crucial to ensuring the bulldozer’s safe operation.
Training and Certification
Operators should undergo comprehensive training and obtain certification to operate bulldozers. This training covers machine handling, safety guidelines, and best practices to maximize efficiency and minimize accidents.
Bulldozer Technology and Innovation
GPS and Automation
Advancements in technology have led to the integration of Global Positioning System (GPS) technology into bulldozers. GPS allows for precise navigation and automated grading, resulting in more accurate and efficient earthmoving operations.
Hybrid and Electric Bulldozers
In response to environmental concerns, manufacturers are developing hybrid and electric bulldozers. These eco-friendly alternatives reduce emissions and lower fuel consumption while maintaining the machine’s high performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Emission Reduction Efforts
Traditional bulldozers emit greenhouse gases and contribute to air pollution. In recent years, manufacturers have been actively working to reduce emissions through improved engine efficiency and cleaner fuel technologies.
Green Bulldozers
The emergence of eco-friendly bulldozers, such as electric and hybrid models, represents a significant step toward sustainability in the construction industry. These machines aim to minimize their ecological footprint while still delivering powerful performance.
The Future of Bulldozers
Potential Advancements
The future of bulldozers looks promising, with ongoing research and development focusing on increased efficiency, automation, and reduced environmental impact. Manufacturers continue to explore novel materials and technologies to make bulldozers even more versatile and eco-friendly.
Industry Trends
As technology evolves, bulldozers will likely become smarter and more interconnected with other construction equipment. Artificial intelligence and data analytics may play a more prominent role in optimizing bulldozer operations and improving project management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bulldozers have proven to be a cornerstone of modern construction, mining, and earthmoving industries, shaping the landscapes we inhabit and contributing to the progress of civilization. From their historical origins as modified farm tractors to the highly advanced machines of today, bulldozers have evolved significantly, embracing technological innovations and environmental considerations.
The advancements in bulldozer technology have significantly enhanced their performance, safety, and efficiency. Hydraulic systems and GPS integration have revolutionized the way operators control these machines, allowing for precise grading and leveling with reduced human error. Moreover, the development of hybrid and electric bulldozers reflects the industry’s commitment to sustainability and reducing carbon footprints.
Crawler bulldozers, with their superior traction and stability, are perfect for heavy-duty applications and challenging terrains. They have become an invaluable asset in mining, construction, and infrastructure development, ensuring tasks are completed efficiently and effectively.
On the other hand, wheeled bulldozers offer enhanced mobility and maneuverability on hard surfaces, making them indispensable for urban construction and road maintenance projects. Their versatility and ability to navigate tight spaces contribute to increased productivity in urban areas.
Both types of bulldozers play crucial roles in land clearing, site preparation, and material handling, depending on the specific requirements of the project. Their use in agriculture, forestry, disaster response, and environmental restoration highlights their adaptability across various sectors.
FAQs
- Q: How fast can a bulldozer travel?
- A: Bulldozer speeds vary depending on the model and terrain, but they typically move at speeds of 3 to 6 miles per hour.
- Q: What is the lifespan of a bulldozer?
- A: The lifespan of a bulldozer can range from 10,000 to 30,000 hours of operation, depending on maintenance and usage.
- Q: Can bulldozers work in extreme weather conditions?
- A: Yes, bulldozers are designed to work in a wide range of weather conditions, from scorching heat to freezing cold.
- Q: How do bulldozer operators ensure precision while grading?
- A: Modern bulldozers equipped with GPS technology allow operators to achieve precise grading by following digital grade designs.
- Q: Are bulldozers used in military applications?
- A: Yes, bulldozers have been adapted for military use, particularly for engineering tasks and clearing obstacles on the battlefield.